California
It’s an exciting time to be an energy-consuming organization in California. That’s because we’re on the cusp of a new era in clean energy. Our drive toward generating 100% of our state’s energy by way of renewable sources by the middle of this century is one no other state can match.
CPower wants to help your organization lead California toward a more sustainable future with demand-side energy management.
CPower can help monetize your energy assets in the Golden State.
Start the Conversation with CPower
Fill out the form below or Call CPower 844-276-9371
About the California Energy Market
California’s wholesale energy market includes a day-ahead process and a real-time process. The products and services traded within the California market help CAISO serve load and meet the state’s reliability needs.
The day-ahead market opens seven days in advance of the targeted trading day and closes at 10 AM on the day before the energy will be used. Through three progressive stages (Market Power Mitigation, Integrated Forward Market, Residual Unit Commitment), the market receives buy and sell bids, guarantees supply will meet demand, clears the price, and settles the transactions.
The real-time market is a spot market in which utilities can buy power to meet the last few increments of demand not covered in their day-ahead schedules. It is also the market that secures energy reserves, available for ISO use if needed, and the energy needed to regulate transmission line stability.
Demand Response Programs in California
Demand Response programs pay organizations for using less energy when the grid is stressed or energy prices are excessively high.
The major underlying value of demand response programs in California is the resource adequacy capacity they provide for the grid.
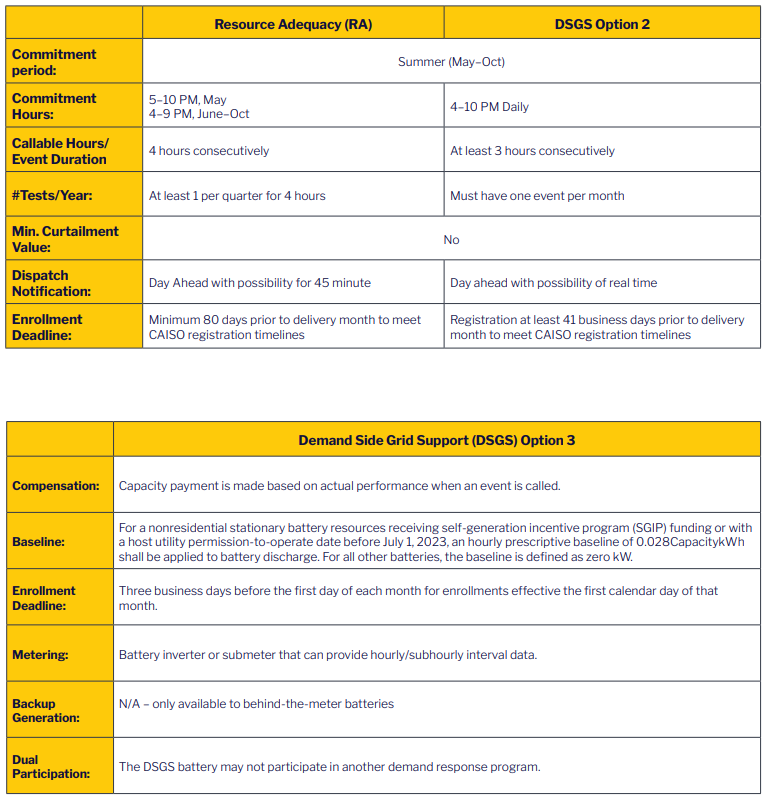
Resource Adequacy (RA) – [Load Serving Entities] ensures there is enough capacity and reserves for the grid operator to maintain a balanced supply and demand across the electric system. During projected tight energy supplies, the ISO will issue a series of emergency notifications to obtain additional capacity or reduce energy use to relieve stress on the power grid.
Demand Side Grid Support Program (DSGS) programs offer several incentive options to electric customers that provide load reduction and backup generation to support the state’s electrical grid during extreme events from May to October, reducing the risk of rotating power outages.
Currently, there are several demand response programs being offered to commercial and industrial organizations in California.