Our Blog On-Demand
Content
Knowledge Hub
Knowledge Hub
As we discussed in our recent blog post about this summer’s potential “perfect Texas storm,” two significant factors projected for the ERCOT (Electric Reliability Council of Texas) energy market could have a noticeable impact on demand response participants: Reduced supply and record peak demand. The resulting clash of supply and demand projections points to the possibility of unexpectedly high prices for those organizations participating in ERCOT’s Load Resources (LR) demand response program.
As we noted last November, ERCOT approved the retiring of three coal-fired generation plants, reducing available generation capacity by about 4,200 MW. In its Final Summer 2018 Seasonal Assessment of Resource Adequacy(SARA), ERCOT projects the Summer 2018 total generation capacity available to be 78,184 MWs, resulting in a capacity reserve margin of roughly 11%. That’s well below its capacity reserve margin target of 13.75% of peak electricity demand.
In a slow economy, reduced supply might not be a problem. But that’s not the case in Texas. The economy is booming in the Lone Star State—in fact, it’s currently the fastest growing economy in the nation. That’s good news for Texans, but not-so-good news for Texans looking forward to a summer of uninterrupted electric supply and the state’s historically low energy prices.
Here’s why. ERCOT predicts “record-breaking peak demand usage” for this summer—72,756 MW. According to the SARA report, that’s more than 1,600 MWs higher than the all-time peak demand record of 71,110 MW set in August 2016.
ERCOT recognizes that this tight margin—a mere 5,428 MWs—might be cutting it too close for comfort. With an eye to grid reliability, it says it could find it necessary to deploy Ancillary Services—Load Response, or LR—and Emergency Response Service (ERS) demand response capacity “to maintain sufficient operating reserves.”
The law of supply and demand usually looks something like this:
Low supply + High demand = High prices
With that in mind, will we see record high prices this summer? The forward ERCOT energy market certainly seems to think so. Projected wholesale energy prices in ERCOT for August 2018 have more than doubled since the 4,200 MWs of generation announced it planned to retire in early 2018.
While the price customers receive for participating in LR is different than the energy price they pay when using energy, there is generally a correlation in that when energy prices rise in ERCOT, LR prices also rise. This is due to the structure of the ERCOT market where lower reserves available typically results in higher energy and LR prices.
As we’ve laid out above, we can expect lower reserves available in ERCOT this summer and therefore higher energy prices than we have historically seen.
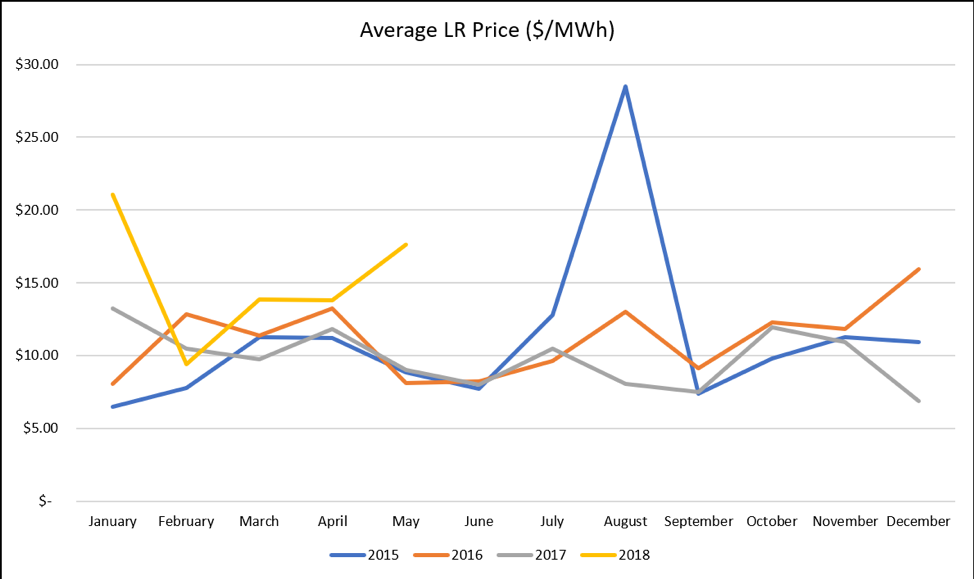
While it remains to be seen if this summer will ultimately result in record high LR prices, we can already see in the above chart that there has been an increase in LR prices since the 4,200 MWs of generation retired in early 2018. Will this trend continue? That largely depends on the weather and generation availability this summer, but a great way to offset the increase in energy prices is through participation in LR which allows you to proactively gain revenue from your energy usage.
Join CPower on Tuesday, June 26, for the third in our ERCOT Webinar Series, “The Perfect Texas Storm: Low Reserves, High Prices, and Record Peak Demand for Summer 2018.” Join CPower’s Texas experts Mike Hourihan and Joe Hayden as they tackle the topics that will impact demand response customers this summer.
The webinar is free and now open for registration.
“The Perfect Texas Storm: Low Reserves, High Prices, and Record Peak Demand for Summer 2018”
Date: June 26, 2018
Time: 10:00-11:00 a.m. Central Time
In October 1991, Hurricane Grace formed near Bermuda and began moving north. At the same time, a massive low-pressure system moved south from Canada. They converged in the North Atlantic, creating a deadly, cataclysmic weather event that was dubbed “the perfect storm,” later immortalized in the film of that name starring George Clooney.
No such weather event (or related George Clooney appearance) is currently predicted for Texas this summer. However, two significant man-made forces are currently converging in the ERCOT (Electric Reliability Council of Texas) energy market: Reduced supply and projected record peak demand. The resulting “perfect storm, Lone Star-style” of clashing supply and peak demand projections has led ERCOT to ask those involved in demand response (as well as generators and transmission owners) to focus on maximizing performance.
Let’s take a look at these two big factors impacting ERCOT this summer. First, supply. In Texas, the name of the game is reliability. To ensure a reliable grid, ERCOT prefers to maintain a capacity reserve margin target of 13.75% of peak electricity demand. These reserves enable them to serve electricity needs in case of unexpectedly high demand or levels of unanticipated outages from generation plants.
As we noted last November, ERCOT approved the retiring of three coal-fired generation plants, reducing available capacity reserves by about 4,200 MW. In its Final Summer 2018 Seasonal Assessment of Resource Adequacy (SARA), ERCOT projects total summer capacity to be 78,184 MWs, and the Summer 2018 planning reserve capacity to be 5,428 MWs, or roughly 11% reserve margin. That’s well below its capacity reserve margin target of 13.75% for peak electricity demand.
Second, demand. Texas currently boasts the nation’s fastest growing economy. Its growth is driven, as Forbes reported in May, by a resurgence in oil and gas drilling in the panhandle as well as growth in manufacturing that outpaced national growth rates in that sector. ERCOT’s SARA report acknowledges that this growing economy will continue to drive demand for electrical power, going as high as 84,814 MWs by 2023.
In fact, ERCOT predicts “record-breaking peak demand usage” for this summer—72,756 MWs. According to the SARA report, that’s more than 1,600 MWs higher than the all-time peak demand record of 71,110 MW set in August 2016.
So—72,756 MWs of demand. 78,184 MWs of capacity, 5,428 MWs of reserve planning capacity… frankly, that’s cutting it pretty close. Maybe tooclose. In fact, ERCOT thinks these tight reserves could trigger the need to deploy Emergency Response Service (ERS) demand response capacity, “to maintain sufficient operating reserves.”
If this happens, it increases the potentialforreal-time emergency events in order to maintain the grid’s reliability. How does this affect ERS participants?
ERS pays organizations like yours for using less energy when the grid is stressed and electricity prices are high. There are two types of ERS programs: ERS 10 and ERS 30, which pay businesses for being available to curtail their electricity load within 10 and 30 minutes respectively. The request to curtail is a referred to as a “called event”.
In the aftermath of the SARA report’s release, our ERCOT office heard from a number of customers who were concerned about the potential for real-time extended events. They feared disruptions to operations and the potential negative impact these disruptions could have on their customers and their bottom line. But how likely are we to see calls to curtail in ERS?
Looking at historical data, not very likely. Called events in ERS are rare. Between 2008 and 2017, a total of three events have been called. In the last eight years, we have seen no events at all. Over the past ten years, capacity shortage events above and beyond annual tests have averaged 0.3 per year in ERS 10, and 0.2 per year in ERS 30. As far as frequency goes, over the last 10 years the most that the ERS program has seen in one year is… two.
Based on the numbers, then, the odds are good that you won’t have to endure many, if any, curtailment requests. We’re confident that you should still be able to participate as in years past, and continue to earn revenue for your availability.
That said, CPower recommends the following steps to maximize your performance in ERS this summer.
Check your plan. Businesses and organizations change, expand, contract, evolve, and are seldom the same year over year. The curtailment plan you first developed with CPower’s engineers may no longer be the best fit for your current electricity usage and operations. Contact CPower and set up a review of your plan. An up-to-date curtailment plan is the best path to success in demand response. (You may even find some additional kWs to enroll that weren’t there before.)
Automate your DR. Automation is required for ERS 10 participation, but it’s still optional in ERS 30. Having even one or two steps on your curtailment process automated can make the difference between performing and underperforming. Make sure you discuss automation opportunities, including incorporating CPower’s Link API, when you review your curtailment plan.
Test your generators—at full load. If you’re counting on your back-up generators to provide you with needed energy during your curtailment events, make sure they can handle the load. Too many generators undergo their monthly and weekly test running off load, for fear of wearing their generators out. The problem is, generators are designed to run at their stated rating, every time. In fact, testing at less than full load can ruin an engine in as little as 50 hours of accumulated running time. Ask CPower’s engineers to review your current onsite generation process as part of your curtailment plan review.
While you’re at it, set up some time to assess your generators for enrollment in demand response. Properly permitted, onsite generation is source of additional revenue. Talk with CPower about your options.
CPower is here to help you through what could be a long, hot summer in the Lone Star State. ERCOT expects everyone, including demand response participants, to give the grid maximized performance for the benefit of all. CPower is here to help you do just that.
Join CPower on Tuesday, June 26, for the third in our ERCOT Webinar Series, “The Perfect Texas Storm: Low Reserves, High Prices, and Record Peak Demand for Summer 2018.” Join CPower’s Texas experts Mike Hourihan and Joe Hayden as they tackle the topics that will impact demand response customers this summer.
The webinar is free and now open for registration.
“The Perfect Texas Storm: Low Reserves, High Prices, and Record Peak Demand for Summer 2018”
Date: June 26, 2018
Time: 10:00-11:00 a.m. Central Time
Big news came out of the PJM Interconnection’s Base Residual Auction (BRA), for the 2021/22 delivery year, two weeks ago. Contrary to what most industry experts and trade journalists had predicted, PJM’s Capacity Performance (CP) emergency demand response program did not fail. In fact, we saw offered and cleared Demand Response megawatts (MWs) increase drastically, the highest volume of Energy Efficiency to ever clear a BRA, and prices came soaring back up, shocking prognosticators everywhere.
Although this may all be contrary to the opinions of the majority in the energy industry, it is right in line with what I highlighted in my white paper from October, 2017, “PJM Capacity Performance is Here. Don’t Believe the Myths.” In it, I outlined three “myths” that were clinging to PJM’s CP-only demand response program and shot each one down. Seven months later, the market has proven us right.
It would be impolite to say, “I told you so.” So instead I’ll show you. Here are the three myths that I discussed, and how the results Wednesday’s auction proved each of them wrong.
Myth #1: Demand Response has declined over the last six years.
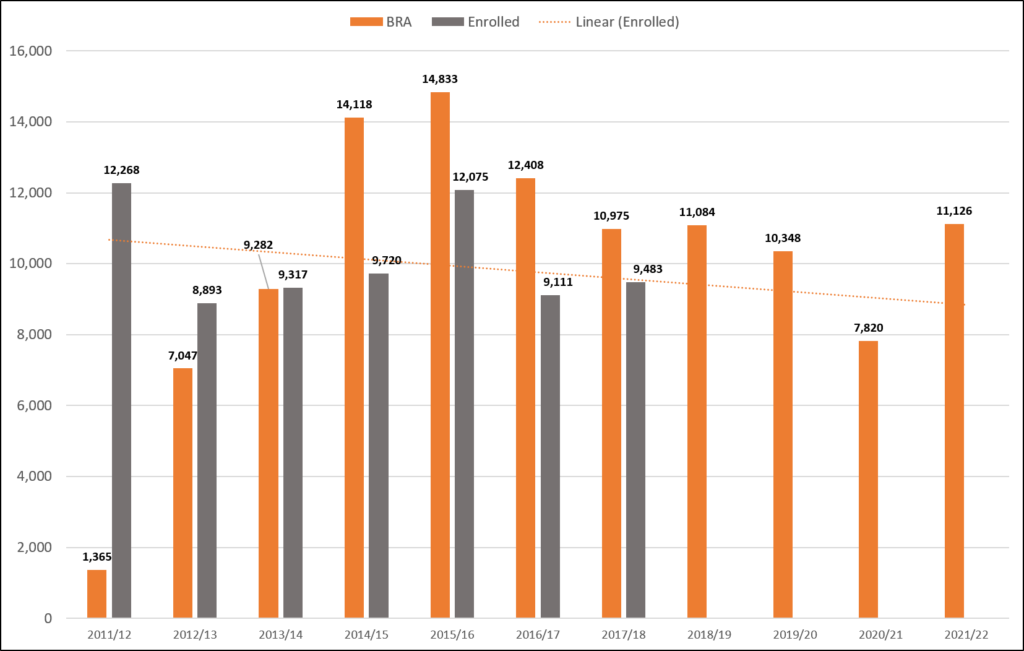
I called this a “pernicious myth that can prevent organizations from opening a rewarding and potentially substantial revenue source.” The idea was cleared capacity was declining, which meant demand response is declining. Not so, I said. There’s a big difference between cleared capacity and enrolled capacity, and while cleared may have seen recent declines, enrolled was remaining steady and strong, which means DR overall remains strong and will continue to be.
Flash forward to Wednesday. The amount of Demand Response that cleared the BRA was 11,125.8 MW. Not only is that about 3,300 MW more than last year’s BRA (the first for CP-only). It is the highest amount of cleared DR in a BRA since the 2016/17 BRA five years ago. Now it remains to be seen if 11,125.8 MW of DR is enrolled in the 21/22 DY, but it’s well within reason to expect ~9,500 MW to be enrolled, which would maintain the amount of participating DR flat YoY.
Myth #2: New CP requirements make it difficult to participate in DR.
In my white paper I stated that although grid reliability is PJM’s number one focus (and rightfully so), and the new CP requirements imposed on Demand Response customers appear daunting (with higher noncompliance penalties and much longer requirements to perform), the impact on DR should be negligible. The implementation of CP to help prevent PJM from entering into emergency situations should mean less of a need for emergency resources such as Demand Response.
It appears that Demand Response customers are adjusting their mindsets from thinking that they can—or only want to—participate in summer-only emergency programs, to understanding that they do have the ability to be year-round resources. And Curtailment Services Providers now believe that they can support a Capacity Performance DR offering and feel there are sufficient customers that can comply and meet their RPM Commitments. This is evident in that over 2,000 MW more DR was offered into the 21/22 BRA than the 20/21 BRA. The DR industry is becoming more comfortable with the Capacity Performance program.
Myth #3: 100% CP means PJM is moving away from DR.
The RPM is an auction-based model that PJM uses to meet forward demand, and it does so by clearing sufficient capacity needed for reliability at the cheapest cost to load. PJM recognizes and understands the value that Demand Response resources bring to the market. The 21/22 BRA cleared at much higher prices across the RTO than nearly everyone projected. And although the prevailing thought is that many capacity resources adjusted and increased their offer prices, which caused prices to spike and PJM to clear Demand Response and Energy Efficiency resources in their place, nonetheless the need for these resources has been proven.
Despite what you may have been told, Demand Response is not back, folks. It never really went away. At CPower we expect the market and the programs to continue to change. It’s what we’ve always seen and are always prepared to see. And we will continue to adapt every step of the way while finding new ways to help customers reduce their costs and generate revenues to strengthen their energy management strategies.
The following is an excerpt from “Monetizing Energy Assets in the Commercial Real Estate Industry: A Complete Guide for Earning Revenue with demand-side energy management” by CPower:
For the past several years, the economic and policy climate of North America has created an impetus for green and sustainable energy-efficient buildings. The commercial real estate (CRE) industry has contributed to this momentum.
Keeping the supreme goal of providing a great tenant experience at the forefront of their operations, commercial real estate facility managers and executives are increasing their focus on energy management plans rooted in a sustainable building philosophy based on cost-effectiveness and energy-optimization.
The CRE industry’s current push toward a more efficient and sustainable future comes at a serendipitous time when energy markets around the country are working to integrate distributed energy resources (DERs) onto their energy grids in an attempt to diversify their fuel mixes.
Right now and for the foreseeable future, grid operators and electric utilities in each of the nation’s six deregulated energy markets have created a wealth of incentive programs to encourage commercial and industrial organizations to help integrate their grids with distributed energy.
CRE organizations with distributed resources at their facilities like backup generators, solar photovoltaic cells, fuel cells, energy storage and more are therefore in a position to reap significant financial benefits by working with a properly licensed company that can help them monetize their existing energy assets.
The Importance of Tenant Experience
No two commercial buildings are alike and every commercial real estate organization is unique. One trait CRE organization’s share, however, is the unwavering desire to provide a great experience for their tenants.
More and more commercial real estate companies are realizing that sound demand-side energy management–the practice of modifying consumer demand for energy–can play an integral part in providing a great tenant experience.
Without satisfied tenants, of course, the CRE industry wouldn’t exist. That’s why every measure a CRE organization explores concerning energy management should be examined through the tenant-experience lens.
Demand for Green Buildings
Utility costs related to energy, water, and waste have a significant impact on a CRE organization’s profits. For decades, CRE organizations have sought to reduce these impacts by making their buildings more efficient and (if at all possible) environmentally friendly.
Green buildings–those which are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient–are estimated to consume 30-50% less energy than non-green buildings. Green buildings also use an average of 40% less water, emit 30-40% less carbon-dioxide, and produce 70% less solid waste.
Green Buildings, Happy Tenants
In the last several years, CRE organizations across North America have recognized the direct correlation between green buildings and tenant attraction.
The increasing popularity of green leases, which include an up-front establishment of sustainability goals and allocation of implementation responsibilities between the owner and the tenant, is proof that the notion of sustainability is a value shared between CRE organizations and the tenants they serve.
Since the Great Recession, many tenants’ business performance has been and continues to be evaluated by customers and investors looking at aspects beyond the strictly-financial. Tenants want to tell the story of their operating in a green building that actively pursues sustainability efforts with a positive effect on the community and the environment.
CRE organizations who oblige will not only provide a superior tenant experience, they’ll also be in a position to monetize their efforts through demand-side energy management.
Energy Assets in the CRE Industry
CRE Organizations that have made their buildings more energy efficient–whether by lighting upgrades, HVAC improvement, or any other measure, may be eligible to earn money for the permanent reduction of their electric demand.
They may already possess energy assets like back-up generators, energy storage, solar generation, and more that can also earn revenue through demand-side energy management.
Getting started
When selecting a company to guide your demand-side energy management, it’s important to consider the company’s scope of demand-side expertise. Do they serve the markets where your properties reside? Does the company specialize in one type of demand-side energy management, or is it equally skilled in a wide range of energy asset monetization practices?
Most importantly, a demand-side energy management partner should earn your trust in every aspect of the relationship your organizations share.
Demand-side energy management is not a one-size-fits-all exercise. No two buildings are alike and every CRE organization is unique in its complexities.
Like your business, your demand-side energy management strategy should evolve and refine over time, forever in pursuit of perfection as energy markets continue to change and your needs as an organization evolve.
Visit https://cpowerenergy.com/commercial-reit-lp to learn more about CPower’s extensive experience in the commercial real estate industry, including how Tishman Speyer Commercial Real Estate earned more than $1.4 million through demand-side management with CPower as their guide.
To read the entirety of “Monetizing Energy Assets in the Commercial Real Estate Industry: A Complete Guide for Earning Revenue with demand-side energy management” click HERE.
Stand anywhere between Fifth Avenue and the Avenue of the Americas from 48th to 51st Street in Midtown Manhattan and you’re bound to see hundreds of passersby gazing at the iconic sights of Rockefeller Center. If Gregg Fischer is one of them, however, he probably won’t be goggling at the usual tourist highlights—Radio City Music Hall, Christie’s Auction House, the skating rink, or NBC’s broadcast studios. He’ll be heading into one of the center’s ten Art Deco buildings to speak face-to-face with a tenant.
To Gregg, the tenant’s experience is everything.
As the Director of Energy Systems for Tishman Speyer Real Estate, Gregg is personally responsible for managing sixty commercial complexes nationwide. The 8.8 million square feet that comprise Rockefeller Center is just a piece of the more than fifty-million square feet of class-A commercial office space and luxury residential properties Gregg oversees.
“Have you ever seen a circus performer who simultaneously spins ten plates on his feet and arms and head? That’s what I feel like every day of my life,” Gregg says, describing his daily mindset in balancing his company’s needs with those of his tenants. “I make sure all the plates don’t crash.”
For Gregg, every day is filled with minute-by-minute communication with both his tenants and their operation, procurement, and accounting staffs and the departments within Tishman Speyer, from his own team in design and construction to property management as well as the company’s partners and investors.
“The more we innovate on the demand-side, the more the grid, our community, and our tenants win.”
—Gregg Fischer, P.E., Director of Energy Systems, Tishman Speyer Commercial Real Estate

A leading owner, developer, operator and fund manager of first-class real estate worldwide, Tishman Speyer believes sound demand-side energy management—the practice of modifying consumer demand for energy—is crucial to providing a stellar tenant experience. “The more we innovate on the demand-side,” Gregg says, “the more the grid, our community, and our tenants win.”
Gregg is quick to point out the fallacy that Class-A tenants breed Class-A headaches. He would know, since the vast majority of Tishman Speyer’s portfolio consists of Class-A commercial office space that houses high-profile tenants and guests on a daily basis. Informing and educating tenants about the types of demand-side energy management their buildings participate in and the benefit their participation has on the grid, environment, and community helps tenants not only cope with the shifts in energy use but embrace them. “Our tenants spend a lot of time at work,” he says. “The more they learn about our energy management practices the more connected they feel to the building. It makes for a better experience.”
Communication and education are the cornerstones of transparency in the commercial real estate industry. While his preferred method of tenant communication is face-to-face and one-on-one, Gregg also employs a host of mixed media approaches to explain why buildings participate in demand-side programs. “We offer free walking tours of our buildings. We do lobby info-graphic signs. We do elevator screen messages. We even have a tenant smartphone application. Communication is the building block to trust and the key to making [demand-side energy management] work.”
Before Tishman Speyer considers any demand-side energy project, Gregg evaluates the project’s potential for tenant and community disturbance and impact, the potential change the project may bring to the building’s asset value, and other aspects that can affect the project such as leasing and contracts as well as incentive programs.
“CPower has experts in every market to help distill down the key details for our national customers. That’s our job.”
–Michael Mindell, Sr. Account Manager, CPower Demand-Side Energy Management
When it comes to introducing and executing demand-side energy management projects at his company’s properties in New York and elsewhere in the country, Gregg isn’t the only one spinning multiple sets of plates. CPower and its team of energy experts are by his side, juggling platefuls of responsibility and communication to help optimize Tishman Speyer’s tenant experience.
A demand-side energy management company that serves more than 1,300 commercial and industrial organizations nationwide, CPower provides customized solutions that combine demand response, demand management, and distributed energy resources tailored to serve the specific needs of a given organization’s facilities. CPower’s creed centers on the conviction that no two buildings are alike and every organization is unique.
Among CPower’s national team is Michael Mindell, a veteran account executive who’s been involved in the demand response industry since 2001, two years after the New York energy market was deregulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. Michael serves as the primary contact for Gregg Fischer and coordinates with CPower’s teams in the various energy markets where Tishman Speyer participates in demand-side energy management to help present to Gregg the key information necessary to make informed decisions in a timely manner.
“The energy industry is highly complex,” Michael says. “Each energy market is different in their regulations and ways they operate their programs. CPower has experts in every market, including regulatory advisors and engineers with experience in hundreds of commercial real estate facilities to help distill down the key details for our national customers. That’s our job.”
“CPower does a great job of understanding things for us in a short amount of time. Then they come to the table with ideas and solutions.” Gregg says of the demand-side energy management company. “Michael and his team are an honest sounding board that helps me see things in a fresh and different way. Our relationship is such that they can offer very upfront opinions that make the case for doing something either weaker or stronger.”
That CPower operates in all six of the country’s deregulated energy markets and has extensive knowledge of the programs and regulations associated with each market is a big advantage when the time comes to evaluate demand-side strategies for Tishman Speyer’s buildings. “I don’t have the time to go through the fine print and evaluate each and every program. I rely on CPower for that. Michael and his team do a great job of digesting the details and explaining which programs in which markets we should be participating in and what the various impacts might be.”
In 2017, its first year working with CPower, Tishman Speyer had 34 commercial properties participating in demand-side programs in two energy markets: New York, where 25% of the company’s global portfolio resides and PJM, home of the world’s largest wholesale energy market. Through demand response programs, which pay organizations for using less energy when the grid is stressed, Tishman Speyer earned nearly $1 million in curtailment revenue during its first year while earnings in PJM approached $400,000.
In 2018, Tishman Speyer will expand its demand-side energy management participation to include the New England market. For Gregg Fischer, the expansion is about more than improving his company’s bottom line. “It’s my responsibility and Tishman Speyer’s responsibility to leverage the benefits of our demand-side energy management into an experience that tenants, visitors, and guests have never seen before.”
To Tishman Speyer, it’s all about the tenant experience.
Properly permitted, your emergency generation—EG—is both a reliability asset and a revenue generator. EG provides a great opportunity to earn revenue and save on energy costs through demand response (DR) and demand management programs.
The path from emergency generation to revenue generation, though, may seem like a complex, confusing, and occasionally contradictory thicket of state and local environmental regulations. Few organizations fully understand the scope and intricacies of EG regulation, which often results in misinformation, missteps, and missed revenue opportunities.
Fortunately, CPower’s extensive experience and knowledge base has led hundreds of organizations through the jumble of regulations and provided a clear path to monetizing EG assets. This webinar covers everything today’s energy managers and engineers need to to know to maximize the benefits of their EG portfolio. It includes:
Join Ray Berkebile, CPower’s nationally recognized EG permitting expert, and CPower engineer Alison Keefe as they lead this in-depth look at how your EG assets can generate revenue for you, too.
Download the slides: Leverage Your Generator Assets To Earn Revenue Webinar (PDF)
With the season’s first snow on the ground and the official start of Winter just days away, it’s a good time to look back at how the PJM Interconnection performed over the summer, and how it’s projected to perform in the months ahead. While we’re at it, let’s look a little further into the future, to the introduction of full-time Capacity Performance in DY 2020/21.
Early summer heat gave way to a milder late summer.
The 2017/18 PJM Summer DR season began with warmer than usual early summer temperatures and system loads. Although typically PJM’s five system peaks occur mid-July through August, this summer we saw two of the system peaks occur in early June and the others in July. Which meant that DR customers needed to be on alert and ready for emergency events earlier in the summer then they are typically used to. Peak shaving customers also had to be ready to predict early peak days and potentially may have missed them. This may mean higher Peak Load Contribution (PLC) values for the next power year. PJM’s Five Coincidental Peaks (5CP) for 2017 that are used to determine capacity costs through PLCs are shown in the table below.
| DATE | HOUR | PJM LOAD (MW) |
| 7/19/2017 | 18 | 145,331 |
| 7/20/2017 | 17 | 145,097 |
| 7/21/2017 | 17 | 142,003 |
| 6/12/2017 | 18 | 140,660 |
| 6/13/2017 | 17 | 138,365 |
The summer ended without PJM declaring any emergency events, which means Limited DR customers needed only to comply with an hourly test event to show program compliance. Extended Summer DR customers still have May 2018 to be on call for any emergency events, and Annual DR and Capacity Performance (CP) DR customers have the balance of the 2017/18 power year to be on call for emergency events.
Colder and snowier winter than last year projected by PJM.
In a recent press release, PJM states that weather patterns indicate a strong likelihood of a continuation of the cool Summer and Fall temperatures into the Winter. This could bring parts of the PJM territory periods of cold polar blasts, and bring greater chances for winter precipitation than we had experienced the past few winters.
But no worries. PJM reminds all end users that although it anticipates a colder winter—and has forecasted peak loads just over 135,000 MW—it has ample resources to meet the needs of the system demand, with just under 185,000 MW of dispatchable generating capacity.
This is good news for Annual and CP DR customers anxious about potential Winter emergency events. Although all DR customers should be prepared to respond if needed and feel confident in their ability to perform, they should take comfort in PJM’s ability to meet demand and avoid the system entering into an emergency situation.
PJM’s Capacity Performance product is the answer to grid reliability.
As you’re probably well aware, PJM ushered in the new Capacity Performance (CP) product at the start of the 2016/17 season and will transition to a full CP-only market starting with the 2020/21 season. This CP product was PJM’s response to the early 2014 extreme winter weather known as the Polar Vortex. That winter exposed threats to PJM’s ability to meet winter demand as many generation units were unavailable or unable to meet system needs. The CP product now imposes greater requirements on all capacity resources to ensure availability and reliability. It is because of the new CP product that PJM feels even more confident in being able to meet both Winter and Summer system needs going forward.
CPower discusses the Capacity Performance product, the new market, and dissects some myths about the product and what it means to the DR community in its White Paper as well as part of its ongoing webinar series. We highly recommend checking both of them out to help answer any questions you may have on the CP program and your ability to participate in it.
To learn more about PJM’s changing market or about how to be better prepared for potential grid instability this summer, contact Dann or any member of the CPower’s PJM Team.