Our Blog On-Demand
Content
Knowledge Hub
Knowledge Hub
The sweltering heat that raged across thirteen western states from August 14-17, 2020, had a significant impact on the tens of millions of people who experienced record high temperatures well above 100°F. The triple-digit temperatures had an historic effect on California’s electric grid, too. Consider August 17 as a case-in-point in the energy deficiency the state’s grid operator faces.
According to CAISO’s market policy and performance vice president, Mark Rothleder, CAISO had expected the load on its grid to peak near 49,800 MW on August 17 during the 5-6 pm PT hour with available capacity near 46,000 MW, leaving a 3,600 MW shortfall.

By 8 pm PT on the 17th, that gap would grow to more than 4,400 MW as peak load approached 47,428 MW, but capacity had fallen to around 43,000 MW due to solar generation declining with the setting sun.
Faced with more inevitable forced outages on August 17, CAISO’s own CEO, Steve Berberich spoke before the ISO’s Board of Governors and said, “The situation could have been avoided,” and further asserted that the state’s resource adequacy program is “broken and needs to be fixed.”
A proposed decision on the future of resource adequacy in California is due in mid-June 2021.
Lack of Imports During the Heatwave
The scorching temperatures drove a massive demand for energy throughout the western US, resulting in California’s inability to import electricity from neighboring states as it typically does in the evenings when its robust solar resources go offline with the setting sun.
In its official analysis, CAISO detailed a series of events explaining how “realtime imports increased by 3,000 MW and 2,000 MW on August 14 and 15, respectively, when the CAISO declared a Stage 3 Emergency.” but ultimately “the total import level was less than the CAISO typically receives.”
Unable to import needed electricity and hamstrung by rising demand amidst record-high temperatures, the California grid suffered its first blackouts in nineteen years.
The Push to Address Climate Change
Californians, by and large, see the recent wildfires and heat waves that have ravaged the Golden State and wreaked havoc on its grid as events driven by climate change.
The state’s drive toward its energy future subsequently involves not only taking steps toward making its grid resilient but doing so in a way that minimizes its climate impacts.
The state’s three main energy organizations–The California Independent System Operator (CAISO), the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC), and the state’s energy commission (CEC)–have been closely examining the recent grid failures and have submitted two reports (Preliminary and Final Root Cause Analysis) seeking to establish a root cause for the blackouts .
While they may not agree on any single culprit for California’s grid woes and for the August blackouts, the big three organizations rightfully believe that establishing grid resilience and serving the state’s ratepayers are the priorities.
Balancing Energy, Capacity, and Renewables for Grid Resiliency
California’s renewable energy resources performed as expected in 2020, despite some slanted media coverage that may have tried to pin them with the lion’s share of the blame for the August blackouts in 2020.
California has no intention of veering from the state’s long-traveled path of developing and integrating more renewable energy into its generation mix.
In the wake of the 2020 blackouts, the resource adequacy proceeding in California is looking at how to ensure that the state procures energy sufficiency-–

i.e. electricity needed to serve the state on a day-by-day, moment-to-moment basis–in addition to capacity sufficiency–i.e. reserves that can be called on in the event of an emergency.
The proceeding is trying to establish the optimal balance between energy and capacity that can be procured within state boundaries so it can then be determined just how much reliance should be placed on imports now and in the future.
As is the case with other states in different energy markets around the US, California is at somewhat of a tipping point with so much of its generation mix dependent on renewables with inherent intermittency that renders them unavailable at unpredictable times in the day when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
Like many grids facing a similar predicament, California’s grid of today and the future needs to ensure that its load begins to follow its supply, meaning that demand-side resources adopt agile flexibility that can react to sudden disruptions in electricity supply due to intermittency.
Those disruptions and foreboding heatwaves show no signs of diminishing in 2021 and beyond. It’s time for California to shore up its grid’s reliability with an energy marketplace that rewards flexible resources on the demand side.
The grid and the people it serves depend on it.
In the mid-1960s, a new method for effectively transmitting electronic data over a computer network was born, and with it came one of the quintessential building blocks of what would become the modern internet.
In simple terms, “packet switching” is a routing method whereby data transmitted across a network takes different routes along the network to arrive at its destination. Packet switching allowed for computer networks to become decentralized, ultimately giving rise to the internet and the global connectivity it provides today.
Just as packet switching would help computer networking explode into the future, so too will a similar decentralization usher the electric grid from what it was for the previous century to a more efficient interaction that connects consumers in a cleaner and more collectively beneficial way.
Like most revolutionary ideas, packet switching was not embraced by the established community of experts that presided over the nascent field of computer networking in 1965. That changed, however, when the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) embraced packet switching as a means to allow multiple computers to communicate on a single network.
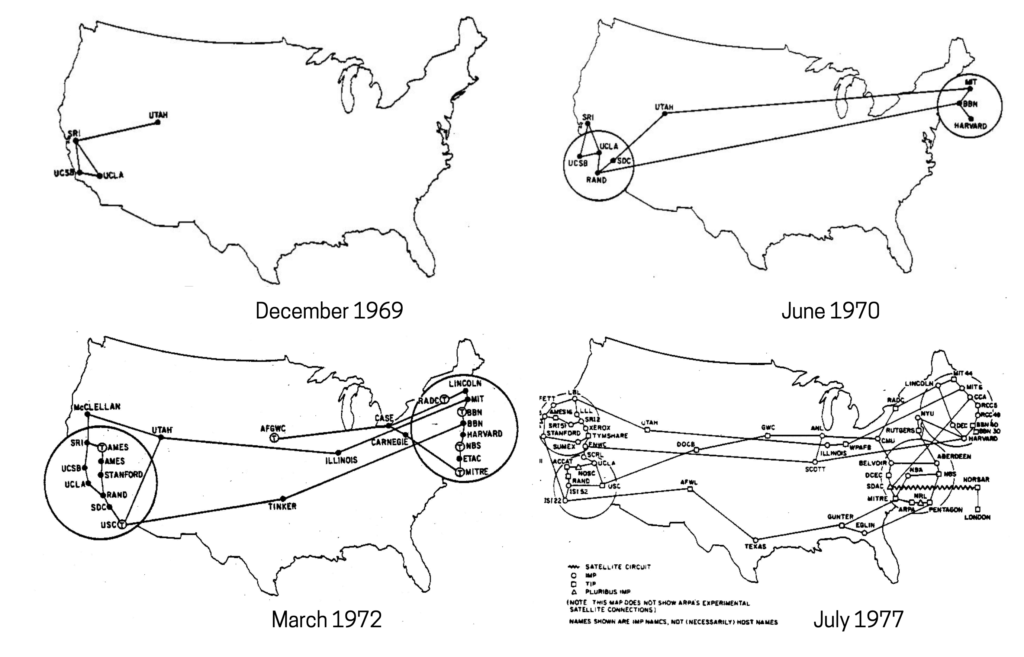
Originally funded by the US Department of Defense and widely considered among historians as the first working prototype of the internet, ARPANET would adopt the internet protocol suite TCP/IP on New Year’s Day in 1983, and begin assembling the network that would become the modern internet.
Since its inception, the grid has grown and evolved to become a modern network on the cusp of transitioning to a more efficient future. To get there, the electric grid may borrow a page from the information superhighway and follow a few key transformational lessons.
Consider how information travels on the internet in 2021.
On the internet, every user is a consumer, producer, and storer of information. Send an email from the Northeast US today, and it might route through Canada on its way to a final destination. Send an email to the same person tomorrow, and it might take an entirely different path through a server in New York.
In essence, this is packet switching on steroids.
The pathways that allow for information to travel on the internet are omnidirectional, which has allowed that network to rapidly grow over the last two decades to serve billions of users worldwide.
That was not always the case if you consider how, prior to packet switching, the original computer networks were constructed as a network dominated by central mainframe servers that pushed information and data to users connected at terminal locations.
The electric grid has a similar history to the internet’s in that the grid’s network was centralized from the outset, with large generation sources (power plants) essentially pushing electricity to consumers via transmission and distribution.
The centralized grid conceived by the likes of Thomas Edison and erected by moguls like George Westinghouse served its users well for the better part of the century.

Like the internet, however, the electric grid has evolved to embrace decentralization as it transitions to an omnidirectional network in which generation and distribution are spurred by the very users for whom the grid exists to serve.
Today, for example, the electricity you use to charge, say, your mobile phone may come from the bulk grid. Tomorrow it could come from another consumer on your distribution grid who is not using their own excess generation.
As grid operators and utilities adopt new technologies to enhance their flexibility and optimize the delivery of electricity, the grid will start to follow a similar path the internet embraced in its evolution to the modern wonder it is today. The result will be an energy system whose connectivity drives its efficiency and sustainability for decades to come.
It’s an exciting time for the grid and its users, rife with possibility and opportunity.
A convergence of pressures in recent years has caused organizations across North America to examine how their energy use can be managed to help achieve their carbon reduction goals.
These converging pressures originate from customers, who desire to do business with sustainability-minded companies; investors, who realize the inherent value associated with an organization being carbon neutral; and regulators, who are introducing laws that reflect and address society’s move toward a cleaner energy future.

Since these pressures show no signs of waning, the question of how exactly demand-side energy management can be optimized to achieve carbon goals is becoming a popular discussion in the industry today.
Some of the best practices for carbon-reducing with demand-side energy management are more obvious than others. Adopting energy efficiency measures or installing on-site renewable energy sources like solar are examples of strategies that have been around for decades.
Let’s examine, then, some of the newer concepts on the topic of achieving carbon goals with demand-side tactics.
Consider the drive toward a carbon-neutral future from the grid operator’s perspective. Across the US, grids face the same converging pressures as organizations and have worked to increasingly shift their generation mixes away from fossil fuels and toward renewable sources like wind and solar.
Of course, wind and solar energy sources are inherently intermittent and can subsequently cease generating if the wind stops blowing or the sun stops shining.
But the immutable truth that some days are overcast and others windless doesn’t ease the pressure on the grid and those who run it to drive toward carbon- neutrality! Nor does inescapable intermittency suffice as an acceptable reason for grid operators to sacrifice reliability in the name of sustainability.
So what’s a grid operator to do?
Here is where commercial and industrial organizations can fill the gap from the demand side and help the US electrical grid find its way to the clean and efficient energy future that everyone desires.
That the grid needs flexible resources which can be dispatched quickly to serve load when it’s needed due to wind and solar generation being unavailable is a central point readers of this book should be quite familiar with, given it’s been examined in detail within these pages over the last three years.
The same is true of the role demand response plays in providing that flexibility to the grid.
What’s becoming more apparent is how increased participation in demand response programs at the ISO and utility levels across the US is providing new tools for grid operators to harmonize their grids’ reliability with their drive toward a future of cleaner generation fuel mixes.
In effect, this demand-side participation enables the firming of renewable energy sources, allowing grids to transition toward cleaner fuel mixes. While demand response participation doesn’t directly help individual organizations achieve their own carbon reduction goals, the cumulative effect of all the organizations’ participation does help our society achieve its desired emission goals.
The pressures organizations face from outside entities that we discussed earlier play a role in driving a given company’s carbon-reduction goals.
Unfortunately, in a reward-based world dominated by measurable metrics, there isn’t a practical way to note just how effective a given organization’s demand response participation is in helping contribute to carbon and greenhouse gas reduction.
That’s starting to change.
Organizations like the non-profit WattTime are searching for and establishing ways to help companies receive measurable recognition for doing their part with demand response to help the grid maintain reliability during its transition to the future.
Naturally, how an organization uses energy can have a large impact on carbon emissions, but when energy is consumed can move the carbon reduction needle, too. By shifting energy usage to a time when the grid mix is cleaner—during the middle of the day when solar is more prevalent compared with coal, for example—overall emissions are lowered.
An increasing number of organizations and cities have sought to eliminate their emissions in the time period when they consume electricity, often in hour-by-hour increments. This is a practice called 24/7 Clean Energy.
The more generation mixes shift toward renewable sources and as more DERs integrate into the grid with help of regulations like FERC Order 2222, the more the 24/7 clean energy effect should increase. That is, an increase in peak renewable generation will likely result in a larger potential emission reduction due to the load having been shifted.
Companies, regulators, and markets are in the early stages of ascribing value to 24/7 clean energy practices.
Consider the New York market, where Local Law 97 (LL97) seeks to reduce carbon emissions in the city’s building stock by 80% by 2050. An estimated 50,000 buildings in New York City stand to be affected by the law, with many in the commercial sector currently above the law’s emission requirements. Retrofits are one means of achieving compliance with LL97. Load shifting may be another, albeit one that will require a tangible means of assigning value to the practice.
Here we have an example of a regulation (LL97) creating a need for a possible market incentive (the value assigned to load shifting) as a means to achieve the societal goal of lowering carbon emissions in a densely populated city.

Absent a concrete policy on climate change at the national level, the market is responding. Throughout each of the deregulated energy markets in the US, demand response programs are growing at the ISO and utility level. The markets are becoming more sophisticated with how they incorporate DERs, and they’re doing all of this at the behest of state legislatures as well as the citizens who the market and grid ultimately serves.
Demand-side resources deliver carbon benefits. They always have, but today more opportunities are emerging to earn revenue with these resources.
For years we’ve touted how flexible resources will help drive the US electric grid to a cleaner future. While the ways organizations that provide those resources will be publicly credited are still undecided, the ways they’ll be financially rewarded are apparent.
This post was excerpted from The State of Demand-Side Energy Management in North America Volume III, a market-by-market analysis of the issues and trends the experts at CPower feel organizations like yours need to know to make better decisions about your energy use and spend.
CPower has taken the pain out of painstaking detail, leaving a comprehensive but easy-to-understand bed of insights and ideas to help you make sense of demand-side energy’s quickly evolving landscape.
The idea that reducing a watt of energy on the demand side can be just as valuable as generating one on the supply side in a time of grid stress is hardly new. Nor is the idea that such a solution helps thwart both energy-related and environmental crises.
The origin of demand response can be traced to roughly forty years ago when both the US and the world grappled with many of the same energy and environmental issues we are still trying to solve today.
Let’s take a trip back to the mid-late 1970s and see if a few things don’t look and sound familiar.
The oil crisis of 1973 sent shockwaves throughout the world, raising concerns on the security of electricity supply in the US while pointing to a need to diversify the nation’s power generation mix away from a fossil fuel dependency and toward a mix with a greater share of renewable and clean energy sources.
Global environmental awareness had grown to a movement large enough to be seized upon by newly-elected American president Jimmy Carter who, within a month of taking office, donned a cardigan sweater, sat before a roaring White House fire, and urged Americans to join him in conserving energy in a nationally-televised fireside chat.
During that broadcast on February 2, 1977, the president related how a particularly harsh winter had depleted the domestic supply of natural gas and fuel oil. He warned of dark consequences that awaited the most powerful country on earth if we as a nation failed to devise a sound energy plan for the future.
Sound familiar?
The 39th POTUS didn’t outright cite demand response as a means to a profitable and sustainable end that night in 1977, but he did allude to the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA), a piece of legislation that would be enacted in 1978 to promote more competitive energy markets in the US by allowing “non-utility generators” to participate in them.
The act would prove to be a landmark piece of legislation, setting the country on the road to conservation and the development of clean and renewable energy sources. It would also open the door to demand response as a viable solution to keeping both the electric grid and the environment in balance.
That open door paved the way for the deregulated, competitive energy markets we have today to replace the vertically-dominated regulatory ones that had existed for most of the 20th century. It also would prove to be the seed that would soon mature and bear the lucrative fruit of modern demand response.
Fast forward back to the present. Federal legislation is still working to ensure energy markets remain competitive with clean and renewable energy sources securing a just and reasonable position place in them.
Order 2222 from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) is a case-in-point. The Order is the latest in a series of directives aimed to create a fair balance between traditional generators on the supply-side and distributed energy resources seeking to enter markets on the demand side.
Issued in September 2020, Order 2222 calls for the removal of “barriers preventing distributed energy resources (DERs) from competing on a level playing field in the organized capacity, energy, and ancillary services markets run by regional grid operators.”
Order 2222, widely hailed as a landmark achievement in the history of the energy industry is about more than just creating more competitive markets. By allowing DERs, including demand response, their just seat in the marketplace, Order 2222 enables the US electric grid to take a giant leap toward a cleaner future.
Consider this recent data on demand response performance in the US:
In 2019, the most recent year for which the data is available, the combined wholesale demand response capacity of all regional system operators in the US grew to 27,000 MW.
How much environmental pollution did all that demand response save the country in 2019 by providing a resource that would have otherwise been supplied by a traditional “peaker” plant?
According to the EPA, the 27,000 MW of capacity from all commercial DR participation in the US in 2019 prevented the greenhouse gas emission equivalent of what an average passenger vehicle would produce were it to drive a little more than 142 million miles.
That same total of reduced load roughly converts to the carbon dioxide emission equivalent of 63 million pounds of coal being burned.
In 2020, CPower’s more than 1,700 customers contributed more than 4,000 MWs of capacity to demand response, effectively reducing the energy equivalent of 7 million pounds of coal that would otherwise have been burned and released into the environment.
Helping the grid stay balanced and keeping the air clean aren’t the only benefits to demand response.
The global demand response market is projected to value at USD $24.71 billion by 2022, an increase from the $5.7 billion valuation of the same market in 2014, according to a recent report published by Million Insights market research firm.
Much has been made in this publication and others in the energy industry about the evolving electric grid and demand response’s role in helping to bridge past, present, and future.
As you read these words, energy markets and electric utilities across America are refining their demand response programs and introducing new ones, providing organizations with a lucrative and socially responsible way to use their energy assets to support grid reliability in this critical time of transition.
America opened the door for demand response nearly forty years ago. Closing it now (even just a little bit) would be a step toward the past in a time when the country should be crossing the bridge to energy’s future.
Good news on the regulatory front for new demand response resources from New York’s zones G-J entering NYISO’s Installed Capacity Market.
On February 18, 2021, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) issued an Order that overturned a portion of its previously issued Oct. 7, 2020 Order in the paper hearing on whether utility demand response programs Commercial System Relief Program (CSRP) and Distribution Load Relief Program (DLRP) are intended to provide benefits solely to the distribution system (i.e. not for providing similar services to wholesale capacity) and whether the revenues from such programs should be included in new Special Case Resources (SCR) entering the market in New York’s ‘Mitigated Capacity Zones’ G-J Offer Floor calculations as part of Buyer-Side Mitigation (BSM).
FERC’s Feb. 18 Order excludes CSRP revenues (in addition to DLRP revenues as the Oct. 7 Order did), making it much more feasible for most new SCRs to pass the Offer Floor test and not have to sell into New York’s installed capacity (ICAP) market at a price point that is unlikely to clear.
Customers located in Mitigated Capacity Zones who are new to the NYISO SCR program are now significantly less likely to 1) be subject to Buyer-Side Mitigation (BSM) and 2) be required to offer to sell capacity at or above an offer floor price that may not clear in the market.
Rather than run the risk of being found subject to buyer-side mitigation and have an offer floor applied (that carries with the Resource until it clears in at least 12, not necessarily consecutive, monthly Spot Auctions), DR participants will no longer need to choose between retail and wholesale markets to provide DR.
Resources capable of providing different types of DR services will be able to realize the full value, benefiting both the bulk power and distribution system operations.
The order helps to unlock the full value stack of wholesale and retail demand response values to participating customers. Subsequently, new demand response customers no longer need to choose between retail and wholesale markets in which to provide demand response resources.
What is Buyer-Side Mitigation?
Buyer-Side Mitigation (BSM) helps maintain the New York energy market’s integrity by preventing power providers from exerting market power by offering into the capacity market at an artificially low price.
BSM helps ensure both energy providers and generators are not able to exercise unfair buyer-side market power—a form of monopoly control over a market.
For example, energy providers that receive “out-of-market” payments such as state subsidies could have an unfair advantage over other power providers who do not receive out-of-market payments when it comes to offering in New York’s capacity market since the subsidized resources could offer into the market at a price that is lower than that of unsubsidized resources.
Allowing subsidized resources to offer into the capacity market at an artificially low price would distort the actual cost and the resulting market price of capacity when power providers compete fairly in the free market.
What is the Offer Floor Test?
Without getting overly complicated with details, the Offer Floor test is used to determine if a given resource is either subject to or exempt from Buyer-Side Mitigation.
NYISO defines the Offer Floor Test’s calculation for new SCRs as follows:
The Offer Floor for a Special Case Resource shall be equal to the minimum monthly payment for providing Installed Capacity payable by its Responsible Interface Party, plus the monthly value of any payments or other benefits the Special Case Resource receives from a third party for providing Installed Capacity, or that is received by the Responsible Interface Party (RIP) for the provision of Installed Capacity by the Special Case Resource, except that it shall exclude the monthly value of any payments or other benefits the Special Case Resource receives from a retail-level demand response program designed to address distribution-level reliability needs that the Commission has, on a program-specific basis, determined should be excluded.
A Brief History of Buyer-Side Mitigation and Special Case Resource in New York
The preceding article’s timeline begins in February 2021 with FERC overturning its October 2020 order. Let’s review how the issue has evolved over the previous thirteen years.
Much of the following has been paraphrased from Section II of Docket No. EL16-92-001-NY Public Service Commission v. NY Independent System Operator
Special Case Resources have been subject to NYISO’s Buyer-Side Mitigation since September 2008. In May 2010, FERC approved an Order that excluded certain payments that an SCR may receive from state-regulated, distribution-level demand response programs.
In March 2015, FERC clarified that it did NOT intend to grant an “exemption for all state programs that subsidize demand response” and further explained that a state “may seek an exemption from the Commission [FERC] pursuant to section 206 of the Federal Power Act if it believes that the inclusion in the SCR Offer Floor of rebates and other benefits under a state program interferes with a legitimate state objective.”
On June 24, 2016, the NYSPSC, the New York Power Authority, the Long Island Power Authority, NYSERDA, the City of New York, AEMA, and NRDC filed the Complaint against NYISO, challenging NYISO’s imposition of BSM on SCRs on the grounds that they interfere with legitimate state objectives. The parties requested a blanket exemption from BSM for all SCRs receiving payments pursuant to a “utility-administered distribution-level Demand Response program.”
The parties requested that the Commission approve an exemption for each of the individual utility-administered, distribution-level programs discussed in the Complaint.
On February 3, 2017, FERC ordered a blanket exemption for all new SCRs, explaining that SCRs had no incentive or ability to affect wholesale market rates. FERC also stated that existing SCRs currently subject to mitigation would not be eligible for the exemption, due to the FERC’s “long-standing practice” of not adjusting mitigation measures after a resource enters the market.
On March 6, 2017, Independent Power Producers of New York, Inc. (IPPNY) filed a request for rehearing, arguing that the SCRs, considered in aggregate, could affect wholesale market rates.
In February 2020, FERC issued an Order revoking the blanket exemption granted in the February 2017 Order.17 FERC also ordered the initiation of a “paper hearing” to determine if any specific New York programs to support SCRs should be exempted.
Peter Dotson-Westphalen coordinated AEMA support on the issue of Buyer-Side Mitigation and Special Case Resources following FERC’s February 2020 ruling and coordinated multiple comment filings with staff from NYPSC, NYSERDA, City of New York, NRDC, and Energy Spectrum. He contributed heavily to the drafting work to the joint comments, as well as the testimony of Katherine Hamilton (on behalf of AEMA) in the paper hearing.
Ohio House Bill 6 had the kind of year that, if it hadn’t taken place during 2020, might have garnered national headlines and caught the attention of Hollywood.
Before we succumb to the temptation of divulging exploitative details–which include outcries of scandal, bribery, corruption, and racketeering–let’s cover the fundamentals of the bill and what they mean to organizations in the Buckeye State looking to monetize their energy efficiency (EE) projects in 2021 and beyond.
HB 6 was enacted into law on Oct. 19, 2019, and requires all energy efficiency (EE) programs offered by electric utilities in Ohio to end by December 31, 2020.
That utility EE programs are no longer offered in 2021 means any rebate rewards offered by utilities are no longer available to organizations who complete or have completed, EE projects.
But that DOES NOT mean that organizations and EE project developers in Ohio who help the electric grid by permanently reducing electric demand are shut out from earning revenue for their efforts.
When one door closes…
In Ohio, organizations and EE project developers can, with the help of a licensed curtailment service provider (CSP), offer their permanently reduced demand (“negawatts”) into PJM’s capacity market, the Reliability Pricing Model.
Once the reduced load is accepted into the market, the organization will earn revenue from PJM for four years after the project was completed.
To learn more about monetizing energy efficiency projects in PJM in the wake of Ohio House Bill 6’s enactment, click here.

To learn more about the wild ride House Bill 6 had, Google it and pick from any number of vitriol-laced articles that show up on the first page.
Fun as it may be to shine a light on the mudslinging around HB 6, it’s not our place at The Current to feed the political maelstrom. We’re here to inform, so you can make educated energy management decisions.
That said, you might want to make sure you do your reading on HB 6 indoors and away from the windows. There is a lot of lightning out there right now.
The largest electric utility in Arizona is making strides toward a more sustainable future and it’s clear demand response is part of the plan.
Arizona Public Service (APS) is the owner and operator of the country’s largest producer of carbon-free electricity–the Palo Verde Generating Station.
Currently, the utility generates clean, reliable electricity for 1.3 million homes and businesses in 11 of Arizona’s 15 counties and boasts a current energy fuel mix that is 50 percent clean.
50 percent clean energy in 2021 is impressive enough, but APS CEO Jeff Guldner sees an even cleaner future and has pledged to cease all coal-fired generation in the APS service territory by 2031 and for the utility’s fuel mix to be 100 percent carbon-free by 2050.
To get there, APS plans to call on a generation portfolio that is 45 percent renewable in just nine years.
To help bridge the present and future, APS is counting on its own Peak Solutions demand response program to ensure its grid remains reliable when stressed with heavy electrical demand.
Launched in 2010, the Peak Solutions program engages commercial and industrial customers in voluntary energy conservation measures when demand for energy peaks on APS’s system, particularly during Arizona’s scorching summers.
The program also helps maintain lower-cost power for all customers.
As APS ramps up its drive to a carbon-free future, they’re also ramping up their demand response program and the financial rewards participating commercial and industrial organizations will earn for voluntarily reducing their electricity consumption when the demand on the APS grid is high.
The APS Peak Solutions aims to include participants both small and large evidenced by its minimum load commitment of just 10 kW instead of the more customary 50 kW minimum required by most commercial demand response programs in the US.
By not having any penalties for non-performance, another atypical demand response program parameter, APS is further making Peak Solutions attractive to organizations who have never before participated in demand response.
APS’s CEO Jeff Guldner knows that plans and programs aren’t enough to attain a sustainable future in Arizona. “Achieving and realizing the full benefits of a completely clean energy mix will take partnership,” he said in APS’s published clean energy commitment document, “It’s something for all of us, by all of us.”
To learn more about demand response and the APS Peak Solutions program, click here.
From grid scale to residential rooftop solar, battery energy storage systems hold the promise of a decentralized, decarbonized, and digitized energy future. They offer operational flexibility, encourage deploying renewable assets, provide financial benefits to owners and third parties alike, and promote both grid stability and customer sustainability. In this new white paper, “Batteries Included: Creating Value with Behind-the-Meter Storage,” Rob Windle, CPower Executive Director, Distributed Resources, discusses the many factors that ensure success for battery energy storage systems.